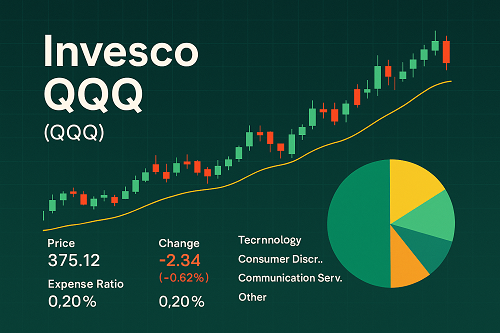
The Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) is among the most active, visible, and impactful exchange-traded funds in the U.S. markets. Tracking the Nasdaq-100 Index (a non-financial subset of the Nasdaq composite), it is heavily tilted toward technology, innovation, and growth names. As such, QQQ often acts as a proxy for “the tech and growth trade” in equities.
- It is highly liquid, making entry and exit relatively efficient.
- It concentrates exposure in mega-cap, high-momentum equities like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Nvidia, and Alphabet.
- For many traders and investors, QQQ is easier to own than picking individual tech names, yet provides broad exposure to leading growth trends.
Because of these characteristics, QQQ is not only a retail favorite but also a key instrument for institutional flows, momentum strategies, and macro overlays. Understanding QQQ—its structure, risks, and behavior—is critical for anyone active in equities, tech, or growth investing.
What Is QQQ? Structure, Index, and Mechanics
Index Tracked: Nasdaq-100
QQQ is designed to replicate the performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index, excluding financial firms. The Nasdaq-100 is composed of 100 of the largest domestic and international nonfinancial companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market, selected by market capitalization.
Important details:
- The index is rebalanced quarterly and reconstituted annually.
- Because the index excludes financials, QQQ tends to be more concentrated in technology, communications, healthcare, consumer discretionary, and similar sectors.
Fund Structure: UIT (Proposed Shift to Open-End)
Since its inception, QQQ has been organized as a unit investment trust (UIT). In this structure, the fund is not permitted to engage in securities lending or reinvest dividends internally; it must distribute cash to shareholders. Invesco+3Investopedia+3Barron’s+3
However, recent developments propose to convert QQQ from its UIT structure into a more flexible open-end ETF structure—a change that would allow:
- Securities lending (which can augment yield)
- More operational flexibility
- Possibly a lower net expense ratio
- Better alignment with other ETFs in the market
Shareholders are scheduled to vote on the proposal.
Expense Ratio, Liquidity & Scale
- QQQ has a total expense ratio of approximately 0.20% annually.
- It is among the most traded ETFs in the U.S. by average daily volume.
- The fund has very large assets under management (AUM), enhancing its stability and liquidity.
- Because of its massive scale, tight spreads, and deep market-making, transaction costs for entry and exit are relatively low compared to smaller ETFs.
Key Metrics & Fundamentals
Understanding QQQ’s key metrics is essential for comparing it with other ETFs, assessing its risk-adjusted return, and identifying when it might be undervalued or overstretched.
| Metric | Typical Value / Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Volatility (1-year) | ~20–25% (annualized) | High volatility compared to broad market indexes |
| Beta (vs. S&P 500) | Around 1.2–1.3 (subject to change) | Indicates QQQ tends to amplify market moves |
| Tracking Error | Low | Because the ETF is passive and well-managed |
| Turnover | Moderate (driven by index rebalancing) | Less frequent trading than actively managed funds |
| Dividend Yield | ~0.5–0.8% (annualized) | Relatively low compared to income or value ETFs |
| Correlation (within tech/growth space) | Very high with mega-cap tech stocks | QQQ often moves in concert with its top holdings |
These metrics imply that QQQ is well-suited for investors who are comfortable with volatility and want high growth exposure, but it is less appropriate for income-seeking or ultra-conservative investors.
Performance & Historical Returns
To evaluate the merit of QQQ, we need to examine its performance over multiple time frames, including drawdowns and cycles.
Long-Term Returns
- Since inception (1999), QQQ has delivered strong cumulative returns, significantly outperforming many broad indexes like the S&P 500.
- Over the past 10+ years, QQQ has consistently exhibited annualized returns in the range of 15–20% (though with periods of volatility).
- For example, as of August 30, 2025 (per Invesco data), QQQ’s 10-year performance stands around 19.4% annualized.
These returns, especially in strong bull markets, have made QQQ a go-to for growth investors.
Cycles & Drawdowns
- QQQ is not immune to deep corrections. For instance, during the dot-com crash, QQQ dropped more than 80%.
- Even more recently, QQQ has experienced drawdowns exceeding 20–30% in market downturns, especially when tech leadership reverses.
- Because QQQ is concentrated in a handful of names, sector rotations away from growth/tech can disproportionately impact QQQ.
Risk-Adjusted Performance
- Over longer horizons, QQQ tends to have favorable Sharpe and Sortino ratios compared with many sector or thematic ETFs—its gains often justify its higher volatility.
- In stable upward trends, QQQ magnifies returns; in downturns, it magnifies losses.
The conclusion: QQQ is a high-risk, high-reward vehicle. It rewards investors during secular bull runs in tech and innovation, but it requires a tolerance for volatility and drawdowns.
Portfolio Composition & Sector Exposure
To understand QQQ’s behavior, one must peer into its holdings and sector weightings.
Top Holdings (As of latest)
QQQ’s top holdings heavily influence its returns. A few names often dominate:
- Apple
- Microsoft
- Amazon
- Nvidia
- Alphabet (Google)
These mega-cap tech names collectively represent a significant portion of the ETF’s total AUM.
Sector Breakdown
While the exact sector weights shift with rebalancing, the general pattern is:
- Technology / Information Technology: largest weight
- Consumer Discretionary & Communications: next most represented
- Healthcare, Consumer Staples, Industrials: smaller allocations
- Minimal or zero in Financials (by design)
- Some foreign exposure is possible, but typically small (e.g. non-U.S. names listed on Nasdaq)
Concentration Risks
Because QQQ invests significantly in its top 5–10 holdings, its returns are partly driven by those few giants. If one or more underperform, it can drag the entire ETF.
Rebalance & Reconstitution Effects
- Quarterly rebalancing can cause buying/selling flows at index bounds, which may generate short-term volatility.
- Annual reconstitution means companies can be added or removed from the Nasdaq-100, which can trigger trading flows and tracking effects.
Risks, Volatility & Drawdowns
No investment is without risk, and QQQ’s profile carries several distinct sources of risk. As a trader/investor, you must be aware of these.
Concentration / Single-Name Risk
Because QQQ leans heavily on mega-cap tech, adverse moves in just one or two names can significantly drag returns.
Sector Rotation Risk
In times of rotation away from growth into value, financials, energy, or cyclical sectors, QQQ tends to underperform broader indices (like the S&P 500 or Russell 2000).
High Volatility & Beta
QQQ typically has a beta above 1 relative to the market, meaning it amplifies market moves. In drawdowns, that means steeper declines.
Liquidity / Market Frictions
Although highly liquid, QQQ still faces intraday volatility and slippage, especially during major macro events or sudden tech shocks.
Tracking Error & Structural Limitations
- From fiscal constraints of its UIT structure
- Lack of securities lending (under current structure)
- Potential change proposals could introduce uncertainty
Regulatory, Macro, and Policy Risks
- Regulations targeting tech, data privacy, antitrust, or geopolitical pressures can disproportionately impact QQQ’s holdings
- Changes in interest rates or macro environment (e.g. inflation, yield curves) tend to penalize growth-intensive portfolios
- Global supply chain disruptions, chip shortages, trade wars, or semiconductor cycles hit the tech core
Dividend Policy & Tax Considerations
Dividend Yield & Payouts
- QQQ pays quarterly distributions, but the yield tends to be modest (typically in the 0.5–0.8% range).
- Because its holdings are growth-oriented (which reinvest earnings rather than paying high dividends), income is not the primary draw.
Tax Efficiency
- Swiss: As a U.S.-domiciled ETF, QQQ distributions are subject to U.S. tax rules for non-U.S. investors.
- ETFs in general have a tax advantage over traditional mutual funds due to in-kind redemptions, which tend to reduce capital gains distributions.
- Under its current UIT structure, QQQ is somewhat constrained in the way it handles dividends and reinvestments, which may reduce flexibility around tax optimization.
- If converted to an open-end ETF, some tax efficiencies (particularly around securities lending revenue) might improve.
Withholding & Foreign Investor Considerations
Foreign investors may face U.S. withholding taxes on dividends. The tax treatment depends on tax treaties, account type (e.g. non-resident vs resident), and local jurisdiction rules. Always consult a tax professional for personal circumstances.
Comparison to Alternatives & Peers
To gauge whether QQQ is the right vehicle, let’s compare it to alternatives in the ETF and index space.
QQQM (Invesco Nasdaq-100 ETF)
- A lower-cost, lower-price-per-share version that also tracks Nasdaq-100
- More retail-friendly in terms of share price
- Slight structural differences, but broadly similar exposure
Broad Market ETFs (SPY, VOO, IVV)
- Much more diversified across sectors
- Lower volatility, lower growth tilt
- Better in value/cyclic rotation phases
Sector/Technology ETFs (XLK, VGT)
- More concentrated in technology or sub-sections
- Higher risk and reward potential
- QQQ provides a hybrid (tech + growth + non-financial exposure)
Leveraged / Inverse ETFs (e.g. TQQQ, SQQQ)
- Provide 2x, 3x leverage for short-term trading
- High tracking error, high risk over long periods
- Useful for tactical trades, not for buy-and-hold
Thematic ETFs (AI, Semiconductors, Cloud)
- More specific exposure (e.g. artificial intelligence, semiconductors)
- Higher risk concentration
- QQQ offers a balanced exposure across many high-innovation names
In many cases, QQQ stands as a “middle ground” — more aggressive than broad market exposure, but more diversified than pure sector or thematic plays.
How to Trade or Invest in QQQ
For Long-Term Investors
- Use QQQ as a core growth equity allocation
- Combine with value, income, or defensive allocations to balance volatility
- Dollar-cost averaging helps mitigate timing risks
- Rebalance occasionally, especially after strong tech runs
For Traders & Active Strategists
- Use technical analysis (trend lines, moving averages, momentum indicators) on QQQ
- Consider options strategies (calls, puts, spreads) around expected volatility or earnings seasons
- Use QQQ as a proxy for tech-sector momentum plays
- Be cautious with leverage—since QQQ is already volatile, adding leverage magnifies risk
Risk Management
- Set stop-losses or trailing stops
- Always compute position sizing consistent with your portfolio risk tolerance
- Be mindful of sector rotation signals (e.g. yield curve changes, macro data)
- Avoid over-leveraging into QQQ unless your risk budget permits
Practical Execution Tips
- Use limit orders rather than market orders to control slippage
- Trade when volume is robust (e.g. U.S. market open or early hours)
- Monitor top constituents—if major holdings report or move, QQQ is likely to follow
- Keep track of rebalancing dates, as these can cause flows and volatility
Recent Developments & Structural Changes
Proposed Structural Shift (UIT → Open-End)
As mentioned, Invesco is seeking shareholder approval to convert QQQ’s structure from a unit investment trust to an open-end fund. If approved, this could:
- Enable securities lending, improving yield
- Allow greater reinvestment flexibility
- Potentially lower the effective expense ratio
- Align QQQ with more standard ETF structures in the market
- Generate new revenue streams for Invesco (e.g. advisory fees)
The vote is scheduled for October 24, 2025.
Market Dynamics & Mega-Cap Leadership
- Over the past few years, performance has increasingly been driven by a handful of mega-cap tech names.
- Earnings, regulation, supply chains, AI cycles, and interest rate sensitivity make these names volatile.
- Sector rotation strategies have at times created meaningful divergences between QQQ and broad indexes.
Competitor Launches & Derivatives
- ETFs like QQQM have been launched to offer alternative entry points with lower per-share prices.
- Aggressive use of derivatives (especially in leveraged ETFs) has made trading around QQQ more tactical.
- New ETFs and thematic strategies compete for investor dollars; QQQ must maintain relevance through performance and innovation.
Macro and Policy Tailwinds / Risks
- Rising interest rates and inflation can pressure high-growth valuations.
- Regulatory scrutiny on Big Tech (antitrust, data privacy) can occasionally roil QQQ’s top holdings.
- Technological disruption cycles (e.g. AI, cloud, semiconductors) drive growth but also create uncertainty.
- Global supply chain risk, semiconductor shortages, and international trade tensions can all disproportionately impact the heavy tech tilt.
Forecasts, Scenarios & Strategy
Below are plausible scenarios for QQQ, along with strategy implications.
Bullish Scenario (Secular Tech Upswing)
- AI, cloud, 5G, semiconductors accelerate adoption
- Earnings growth in mega-cap tech remains strong
- Interest rates stabilize or even decline
- Policy environment remains favorable
Implication: QQQ may outperform broader indices, and aggressive growth allocations may reward investors willing to ride volatility.
Base / Neutral Scenario
- Tech growth continues, but moderates
- Broader markets rotate between value/growth phases
- Mild macro headwinds (inflation, supply chain) persist
Implication: QQQ delivers solid returns but with volatility; blending with defensive or value allocations helps stability.
Bearish Scenario (Growth Reversion)
- High rates erode valuations, especially for growth stocks
- Regulatory or geopolitical shocks hit big tech
- Sector rotation away from tech toward value, financials, industrials
- Earnings disappointments in key holdings
Implication: QQQ may underperform or suffer large drawdowns. Hedging or tactical reduction might be warranted.
Strategy Alignment
- Tactical traders: Use momentum, options, and trend signals to ride or hedge QQQ direction.
- Long-term investors: Use QQQ as a growth core but reallocate or hedge in turbulent periods.
- Blended strategies: Combine QQQ with value, dividend, or defensive ETFs to smooth volatility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is QQQ a good buy for long-term passive investors?
A: It depends on your risk tolerance. Over long periods, QQQ has offered exceptional returns, but with volatility. It can serve as a core growth allocation if you’re comfortable riding through drawdowns.
Q: How does QQQ compare to SPY or VOO?
A: QQQ is more aggressive. SPY/VOO provide broad-market exposure; QQQ is more growth/tech concentrated. In value or rotation phases, QQQ can lag.
Q: What about taxes on QQQ for Canadian investors?
A: As a U.S. domiciled ETF, U.S. withholding tax may apply to dividends, and Canadian tax rules would govern capital gains or foreign income. Check cross-border tax treaties and local legislation.
Q: Will converting QQQ to open-end improve performance?
A: Possibly. If securities lending is enabled and expense structures optimized, yield and after-fee returns might improve. But structural changes come with transition risk.
Q: How often should you rebalance to QQQ?
A: If using QQQ within a broader portfolio, rebalancing annually or semi-annually is reasonable, particularly after large tech runs or corrections.
Q: Is QQQ too expensive (0.20%)?
A: In a world where passive expenses can go near zero, 0.20% is not trivial. But for the liquidity, scale, and access to mega-cap growth, many investors find it acceptable.
Conclusion
The Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ) is more than just an ETF; it’s a major barometer of growth, innovation, and tech leadership in capital markets. Its performance over the last two decades has been impressive, but the path has been bumpy, and future returns will depend as much on macro, policy, and innovation cycles as on stock picking.
For traders, QQQ provides a liquid, deep instrument to play momentum or tech rotations. For investors, it offers concentrated access to the engines driving modern markets. But with power comes risk—volatility, concentration, and structural constraints are real.


 XAUT-USD
XAUT-USD AMD
AMD MARA
MARA SHOP
SHOP BULL
BULL CL=F
CL=F